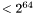 ). In this case there will be no heap allocations done and alle calculations will be done entirely on the stack, as long as they don't exceed the limb size.
). In this case there will be no heap allocations done and alle calculations will be done entirely on the stack, as long as they don't exceed the limb size.
#include <symbolism/N.h>
Members | |
| typedef mp_limb_t | limb_t |
| The type of the digits in the large number. | |
| typedef long unsigned int | size_t |
| The type of the arrays size. | |
| static const int | bits_per_limb = 8 * sizeof(limb_t) |
| Constant representing the number of bits in a limb_t. | |
| size_t | size |
| The number of limbs minus one. | |
| union { | |
| limb_t limb | |
| If size is zero then limb contains the entire integer. | |
| limb_t * data | |
| Array of limbs representing the integer. If size >= 1 then data will contain an allocated array of size + 1 limbs representing the integer from least significant limb data[0] to the most significant limb data[size]. | |
| }; | |
Constructors and Destructors | |
| N () | |
| N (const N ©) | |
| N (const limb_t value) | |
| ~N () | |
Basic operations | |
| limb_t * | limbs () |
| const limb_t * | limbs () const |
| void | set (const N ©) |
| void | set (const limb_t value) |
| N & | operator= (const N ©) |
| N & | operator= (const limb_t value) |
| void | reserve (size_t newsize) |
| Reserve space for newsize limbs. | |
| void | resize (size_t newsize) |
| Resize the integer to use newsize limbs. | |
| void | truncate (size_t newsize) |
| Truncate the integer to use newsize limbs. | |
| void | normalize () |
| Normalize the number. | |
| void | swap (N &a, N &b) |
| size_t | max (const size_t a, const size_t b) |
| Returns the greatest of two N::size_t's. | |
Comparisson operations | |
| bool | is_zero () const |
| bool | is_one () const |
| int | compare (const N &a) const |
| int | compare (const limb_t a) const |
| bool | operator== (const N &a, const N &b) |
| bool | operator!= (const N &a, const N &b) |
| bool | operator> (const N &a, const N &b) |
| bool | operator>= (const N &a, const N &b) |
| bool | operator< (const N &a, const N &b) |
| bool | operator<= (const N &a, const N &b) |
Binary operations | |
| size_t | two_multiplicity () const |
| Returns the number of trailing zeros in the binary representation. | |
| void | binary_not (const N &a) |
| void | binary_not () |
| void | binary_and (const N &a, const N &b) |
| void | binary_and (const N &a) |
| void | binary_or (const N &a, const N &b) |
| void | binary_or (const N &a) |
| void | binary_xor (const N &a, const N &b) |
| void | binary_xor (const N &a) |
| void | left_shift (const N &a, unsigned int count) |
| void | left_shift (unsigned int count) |
| void | right_shift (const N &a, unsigned int count) |
| void | right_shift (unsigned int count) |
| N & | operator<<= (const limb_t count) |
| N & | operator>>= (const limb_t cout) |
| N & | operator &= (const N &a) |
| N & | operator|= (const N &a) |
| N | operator~ (const N &a) |
| N | operator & (const N &a, const N &b) |
| N | operator| (const N &a, const N &b) |
| N | operator<< (const N &a, unsigned int count) |
| N | operator>> (const N &a, unsigned int count) |
Addition operations | |
| void | add (const N &a, const N &b) |
| void | add (const N &a) |
| void | add_one () |
| N & | operator+= (const N &rhs) |
| N & | operator++ () |
| N | operator++ (int) |
| N | operator+ (const N &a, const N &b) |
Substraction operations | |
| void | sub (const N &a, const N &b) |
| void | sub (const N &a) |
| void | sub_one () |
| N & | operator-= (const N &rhs) |
| N & | operator-- () |
| N | operator-- (int) |
| N | operator- (const N &a, const N &b) |
Multiplication operations | |
| void | mul (const N &a, const N &b) |
| void | mul (const N &a) |
| N & | operator *= (const N &rhs) |
| N | operator * (const N &a, const N &b) |
Combined addition and multiplication operations | |
| void | addmul (const N &a, const limb_t b) |
| void | submul (const N &a, const limb_t b) |
Division operations | |
| void | exact_div (const N &a, const N &b) |
| void | exact_div (const N &a) |
| void | div (N &rem, const N &a, const N &b) |
| void | div (N &rem, const N &a) |
| void | quo (const N &a, const N &b) |
| void | quo (const N &a) |
| void | rem (const N &a, const N &b) |
| void | rem (const N &a) |
| N & | operator/= (const N &rhs) |
| N & | operator%= (const N &rhs) |
| N | operator/ (const N &a, const N &b) |
| N | operator% (const N &a, const N &b) |
| N | div (N &rem, const N &a, const N &b) |
| N | div_exact (const N &a, const N &b) |
| N | quo (const N &a, const N &b) |
| N | rem (const N &a, const N &b) |
GCD algorithm selectors | |
| void | gcd (const N &a, const N &b) |
| void | gcd (const N &b) |
| void | extended_gcd (N &x, N &y, const N &a, const N &b) |
| void | lcm (const N &a, const N &b) |
| void | lcm (const N &b) |
Random | |
| void | random (const size_t newsize) |
| void | random2 (const size_t newsize) |
Output | |
| limb_t | to_int () const |
| std::string | to_binary () const |
| std::string | to_hexadecimal () const |
| std::string | to_decimal () const |
| std::string | to_english () const |
| void | write_english (std::ostream &out) const |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &out, const N &n) |
Basic algorithms | |
| void | reserve_small (size_t newsize) |
| void | reserve_large (size_t newsize) |
| void | resize_small (size_t newsize) |
| void | resize_large (size_t newsize) |
| void | truncate_large (size_t newsize) |
| void | normalize_large () |
Binary algorithms | |
| size_t | two_multiplicity_large () const |
| size_t | two_multiplicity_small () const |
| void | left_shift_large (const N &a, unsigned int count) |
| void | left_shift_small (const limb_t a, unsigned int count) |
| void | left_shift_large (unsigned int count) |
| void | left_shift_small (unsigned int count) |
| void | right_shift_large (const N &a, unsigned int count) |
| void | right_shift_small (const limb_t a, unsigned int count) |
| void | right_shift_large (unsigned int count) |
| void | right_shift_small (unsigned int count) |
Addition algorithms | |
| void | add_carry_small (const limb_t carry=1) |
| void | add_carry_large (const limb_t carry=1) |
| void | add_large_large (const N &a, const N &b) |
| void | add_large_small (const N &a, const limb_t b) |
| void | add_small_small (const limb_t a, const limb_t b) |
| void | add_large_large (const N &a) |
| void | add_large_small (const limb_t a) |
| void | add_small_large (const N &a) |
| void | add_small_small (const limb_t a) |
| void | add_one_large () |
| void | add_one_small () |
Substraction algorithms | |
| void | sub_large_large (const N &a, const N &b) |
| void | sub_large_small (const N &a, const limb_t b) |
| void | sub_small_small (const limb_t a, const limb_t b) |
| void | sub_large_large (const N &a) |
| void | sub_large_small (const limb_t a) |
| void | sub_small_small (const limb_t a) |
| void | sub_one_large () |
| void | sub_one_small () |
Multiplication algorithms | |
| void | mul_large_large (const N &a, const N &b) |
| void | mul_large_small (const N &a, const limb_t b) |
| void | mul_small_small (const limb_t a, const limb_t b) |
| void | mul_large_large (const N &a) |
| void | mul_large_small (const limb_t a) |
| void | mul_small_large (const N &a) |
| void | mul_small_small (const limb_t a) |
Addmul and submul algorithms | |
| void | addmul_large_large (const N &a, const limb_t b) |
| void | addmul_large_small (const limb_t a, const limb_t b) |
| void | addmul_small_large (const N &a, const limb_t b) |
| void | addmul_small_small (const limb_t a, const limb_t b) |
| void | submul_large_large (const N &a, const limb_t b) |
| void | submul_large_small (const limb_t a, const limb_t b) |
| void | submul_small_large (const N &a, const limb_t b) |
| void | submul_small_small (const limb_t a, const limb_t b) |
Division algorithms | |
| void | exact_div_large_large (const N &a, const N &b) |
| void | exact_div_large_small (const N &a, const limb_t b) |
| void | exact_div_small_small (const limb_t a, const limb_t b) |
| void | exact_div_large_large (const N &b) |
| void | exact_div_large_small (const limb_t b) |
| void | exact_div_small_small (const limb_t b) |
| void | div_large_large (N &rem, const N &a, const N &b) |
| void | div_large_small (N &rem, const N &a, const limb_t b) |
| void | div_small_large (N &rem, const limb_t a, const N &b) |
| void | div_small_small (N &rem, const limb_t a, const limb_t b) |
| void | div_large_large (N &rem, const N &b) |
| void | div_large_small (N &rem, const limb_t b) |
| void | div_small_large (N &rem, const N &b) |
| void | div_small_small (N &rem, const limb_t b) |
| void | quo_large_large (const N &a, const N &b) |
| void | quo_large_small (const N &a, const limb_t b) |
| void | quo_small_large (const limb_t a, const N &b) |
| void | quo_small_small (const limb_t a, const limb_t b) |
| void | quo_large_large (const N &b) |
| void | quo_large_small (const limb_t b) |
| void | quo_small_large (const N &b) |
| void | quo_small_small (const limb_t b) |
| void | rem_large_large (const N &a, const N &b) |
| void | rem_large_small (const N &a, const limb_t b) |
| void | rem_small_large (const limb_t a, const N &b) |
| void | rem_small_small (const limb_t a, const limb_t b) |
| void | rem_large_large (const N &b) |
| void | rem_large_small (const limb_t b) |
| void | rem_small_large (const N &b) |
| void | rem_small_small (const limb_t b) |
GCD algorithms | |
| void | gcd_large_large (const N &a, const N &b) |
| void | gcd_large_small (const N &a, const limb_t b) |
| void | gcd_small_small (const limb_t a, const limb_t b) |
| void | gcd_large_large (const N &b) |
| void | gcd_large_small (const limb_t b) |
| void | gcd_small_large (const N &b) |
| void | gcd_small_small (const limb_t b) |
GCD operators | |
| N | gcd (const N &a, const N &b) |
N is designed to be a general purpose Arbitrary-precision integer (also known as bignum) class. "Integer" in this case means positive integers including zero.
Internally the number is represented by an array of "limbs", which are 32 or 64 bit long on modern cpu's. The array can be accessed with the function limbs(). The limbs are stored from least significant to most significant.
A optimization is done when the number fits in a single limb (the number is  ). In this case there will be no heap allocations done and alle calculations will be done entirely on the stack, as long as they don't exceed the limb size.
). In this case there will be no heap allocations done and alle calculations will be done entirely on the stack, as long as they don't exceed the limb size.
For numbers of multiple limbs the class relies on the low-level algorithms of GMP. These are reliable and give near optimal performance on most CPU's.
The design goals of the N class are
Most operations, like addition and multiplication are designed in two parts. The raw algorithms, the algorithm selectors and overloaded operators. All these functions come in two flavors, in place and out of place.
Let's take multiplication as an example. The algorithm selectors are:
void mul(const N& a, const N& b)void mul(const N& a)
The first is the out-of-place flavor, it sets the current N (the "this" object) to the product of a and b. For example, to store the product of x and y in z you could write: z.mul(a, b) The three variants are type-overloaders. They allow you to use litteral numbers as arguments: z.mul(a, 5).
The last three are in-place algorithms, to multiply x by y and store the result in x you could write x.mul(y).
The algorithm selectors are called "selectors" because they look at the size of the numbers and select the appropriate algorithm. mul(a, b) for example, will do a direct calculation if both numbers are of native cpu size, otherwise it will call an appropriate GMP function.
All the selectors are marked inline to benefit from constant propagation, if this is properly done the selection is made at compile time and the overhead vanishes.
The size is only limited by the available memmory of the computer. Theoretically, for a 64-bit machine, the maximum integer is
![\[ 2^{64 \cdot 2^{64}} \approx 10^{3.6 \cdot 10^{20}} \mbox{.} \]](form_1.png)
In practice no machine will get close to this limit. Experiments on my 2GB ram 64-bit laptop give an upper bound of approximately
![\[ 2^{268435456} \approx 10^{80807124} \mbox{.} \]](form_2.png)
Calculations should be safe until around a milliamilliatillion 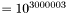 .
.
N mersenne;
mersenne = 1;
mersenne <<= 32582657;
mersenne -= 1;
mersenne.write_language(cout);
mul_<size of operant a>_<size of operant b> where the size of an operant is "small" when it is only a single limb, and "large" when it is at least two limbs.
Again, there are two flavors, in-place and out-of-place. The out of place flavors come in four variants or three when the operation is commutative. In-place operations are never commutative so they always come in four variants.
Definition at line 161 of file N.h.
| typedef mp_limb_t limb_t |
| void reserve | ( | size_t | newsize | ) | [inline] |
Reserve space for newsize limbs.
Allocate memory for newsize limbs, if newsize is zero, all memory is deallocated and limb can be used safely.
| newsize | The required size of the number. newsize is measured as number of limbs - 1. |
The N is not normalized.
Definition at line 554 of file N.h.
Referenced by N::gcd_large_large().
| void resize | ( | size_t | newsize | ) | [inline] |
Resize the integer to use newsize limbs.
Contrary to reserve this function preserves the value of the integer. This means it is not possible to decrease the size of the integer, doing so will result in an exception.
The number is padded with leading zero's to fit the new size.
| newsize | The size the N should become. |
| void truncate | ( | size_t | newsize | ) | [inline] |
Truncate the integer to use newsize limbs.
Just like resize, this function changes the numbers of limbs while perserving the value. The difference is that truncate will allow shrinking the number by throwing away the most significant limbs until the new size is reached.
If newsize > size the number is padded with leading zero's to fit the new size. If newsize < size the number is the most significant limbs are thrown away.
| newsize | The size the N should become. |
Definition at line 617 of file N.h.
Referenced by N::gcd_large_large().
| void normalize | ( | ) | [inline] |
Normalize the number.
This function normalizes the N by removing all leading zero's in the limb representation. If the result is a single limb the N will become small.
Most algorithms have maximal performance when N is normalized. All algorithms are designed to perserve normalization unless otherwise noted.
| size_t two_multiplicity | ( | ) | const [inline] |
| void truncate_large | ( | size_t | newsize | ) |
Definition at line 7 of file N.GCD.cpp.
References N::limbs(), N::reserve(), N::right_shift_large(), N::size, N::truncate(), and N::two_multiplicity_large().
const int bits_per_limb = 8 * sizeof(limb_t) [static] |
The number of limbs minus one.
Definition at line 177 of file N.h.
Referenced by N::gcd_large_large(), and N::truncate_large().
If size is zero then limb contains the entire integer.
Definition at line 183 of file N.h.
Referenced by N::truncate_large().
Array of limbs representing the integer. If size >= 1 then data will contain an allocated array of size + 1 limbs representing the integer from least significant limb data[0] to the most significant limb data[size].
Definition at line 190 of file N.h.
Referenced by N::truncate_large().
Copyright © 2007-2008 Remco Bloemen.
Generated on Tue Jan 22 17:35:31 2008 for symbolism by doxygen 1.5.4